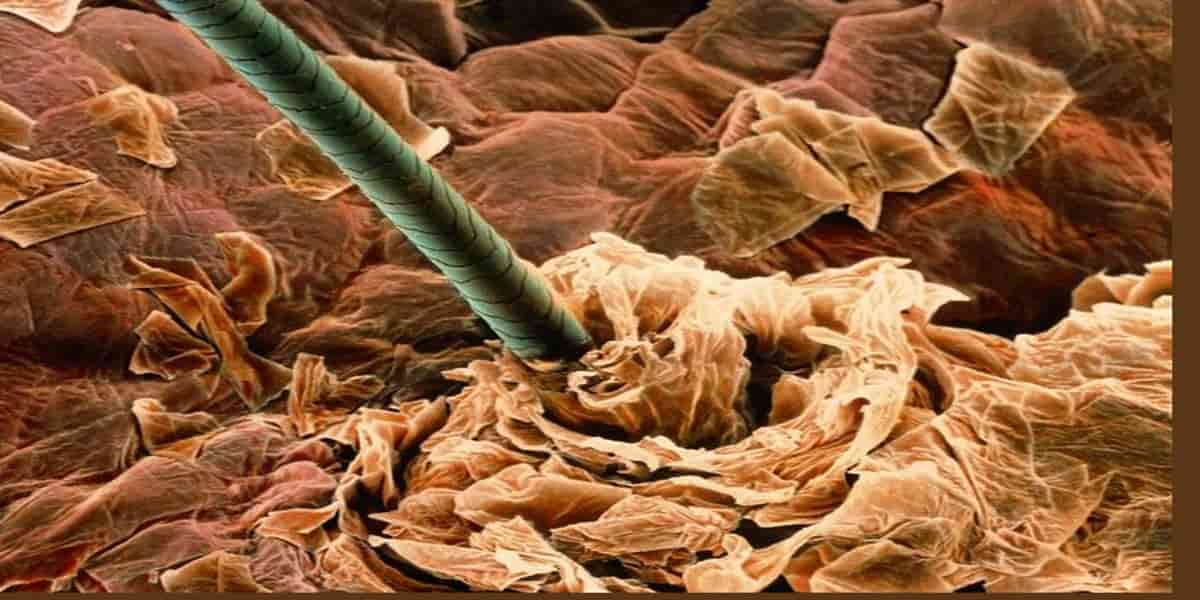
Skin: Largest Organ of Human Body
Doodlebrary
- The skin is indeed the largest organ in the human body.
- It serves several important functions, including:
- Protection: The skin acts as a barrier that protects the body from physical injuries, harmful microorganisms, and environmental factors like UV radiation and pollutants.
- Regulation: It helps regulate body temperature by sweating and controlling blood flow to the skin’s surface.
- Sensation: The skin is equipped with numerous sensory receptors that allow us to perceive sensations like touch, pressure, temperature, and pain.
- Excretion: Small amounts of waste products and toxins are eliminated through sweat glands in the skin.
- Immune function: The skin plays a role in the body’s immune system by serving as a defense against infections.
- The skin consists of three main layers: the epidermis (outermost layer), the dermis (middle layer), and the subcutaneous tissue (hypodermis, innermost layer).
- Each of these layers has its own specific functions and characteristics.
- Overall, the skin is a complex and vital organ that plays a crucial role in maintaining the body’s health and well-being.